<th>: The Table Header element
Baseline Widely available
This feature is well established and works across many devices and browser versions. It’s been available across browsers since July 2015.
The <th> HTML element defines a cell as the header of a group of table cells and may be used as a child of the <tr> element. The exact nature of this group is defined by the scope and headers attributes.
Try it
Attributes
This element includes the global attributes.
abbr-
A short, abbreviated description of the header cell's content provided as an alternative label to use for the header cell when referencing the cell in other contexts. Some user-agents, such as speech readers, may present this description before the content itself.
colspan-
A non-negative integer value indicating how many columns the header cell spans or extends. The default value is
1. User agents dismiss values higher than 1000 as incorrect, defaulting such values to1. headers-
A list of space-separated strings corresponding to the
idattributes of the<th>elements that provide the headers for this header cell. rowspan-
A non-negative integer value indicating how many rows the header cell spans or extends. The default value is
1; if its value is set to0, the header cell will extends to the end of the table grouping section (<thead>,<tbody>,<tfoot>, even if implicitly defined), that the<th>belongs to. Values higher than65534are clipped at65534. scope-
Defines the cells that the header (defined in the
<th>) element relates to. Possible enumerated values are:row: the header relates to all cells of the row it belongs to;col: the header relates to all cells of the column it belongs to;rowgroup: the header belongs to a rowgroup and relates to all of its cells;colgroup: the header belongs to a colgroup and relates to all of its cells.
If the
scopeattribute is not specified, or its value is notrow,col,rowgroup, orcolgroup, then browsers automatically select the set of cells to which the header cell applies.
Deprecated attributes
The following attributes are deprecated and should not be used. They are documented below for reference when updating existing code and for historical interest only.
alignDeprecated-
Specifies the horizontal alignment of the header cell. The possible enumerated values are
left,center,right,justify, andchar. When supported, thecharvalue aligns the textual content on the character defined in thecharattribute and the offset defined by thecharoffattribute. Use thetext-alignCSS property instead, as this attribute is deprecated. axisDeprecated-
Contains a list of space-separated strings, each corresponding to the
idattribute of a group of cells that the header cell applies to. Use thescopeattribute instead, as this attribute is deprecated. bgcolorDeprecated-
Defines the background color of the header cell. The value is an HTML color; either a 6-digit hexadecimal RGB code, prefixed by a '
#', or a color keyword. Other CSS<color>values are not supported. Use thebackground-colorCSS property instead, as this attribute is deprecated. charDeprecated-
Does nothing. It was originally intended to specify the alignment of the content to a character of the header cell. Typical values for this include a period (
.) when attempting to align numbers or monetary values. Ifalignis not set tochar, this attribute is ignored. charoffDeprecated-
Does nothing. It was originally intended to specify the number of characters to offset the header cell content from the alignment character specified by the
charattribute. heightDeprecated-
Defines a recommended header cell height. Use the
heightCSS property instead, as this attribute is deprecated. valignDeprecated-
Specifies the vertical alignment of the header cell. The possible enumerated values are
baseline,bottom,middle, andtop. Use thevertical-alignCSS property instead, as this attribute is deprecated. widthDeprecated-
Defines a recommended header cell width. Use the
widthCSS property instead, as this attribute is deprecated.
Usage notes
- The
<th>may only be used within a<tr>element. - In simple contexts, using the
scopeattribute on header cells (<th>elements) is redundant becausescopeis inferred. However, certain assistive technologies may fail to infer correctly, so specifying header scope may improve user experiences. -
When using the
colspanandrowspanattributes to span header cells across multiple columns and rows, cells without these attributes defined (with a default value of1) are automatically fitted into free available spaces in the table structure that span 1x1 cells, as illustrated in the following figure: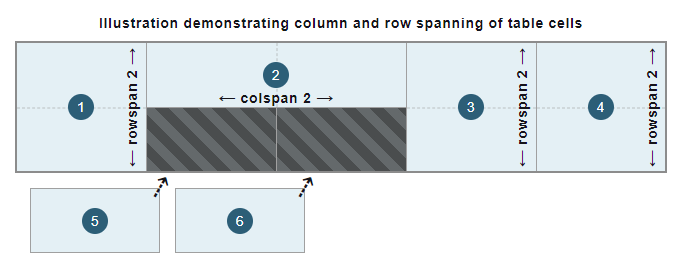
Note: These attributes must not be used to overlap cells.
Examples
See <table> for a complete table example introducing common standards and best practices.
Basic column and row headers
This example uses <th> elements to introduce column and row headers in a basic table structure.
HTML
The first row (<tr> element) contains the column headers (<th> elements), which act as "titles" for the columns to make it easier to understand the information in the columns and identify the data. To indicate that each column header relates to all cells in the corresponding column, the scope attribute is set to col (column).
The remaining rows contain the main data of the table. Each of these rows has a row header (<th> element) introduced as the first cell. This creates a column with row headers as the first column of the table. Similar to the column headers, the scope attribute is set to row to specify which cells each row header relates to, which in the example below are all data cells (<td> elements) in each row.
Note: Normally, the grouping elements <thead> and <tbody> are used to group rows with headers into the respective table head and body sections. These elements are omitted in this example to reduce complexity and enable focusing on the use of header cells.
<table>
<tr>
<th scope="col">Symbol</th>
<th scope="col">Code word</th>
<th scope="col">Pronunciation</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<th scope="row">A</th>
<td>Alfa</td>
<td>AL fah</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th scope="row">B</th>
<td>Bravo</td>
<td>BRAH voh</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th scope="row">C</th>
<td>Charlie</td>
<td>CHAR lee</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th scope="row">D</th>
<td>Delta</td>
<td>DELL tah</td>
</tr>
</table>
CSS
Some basic CSS is used to style the table and its cells. We use CSS attribute selectors to target header cells based on their scope attribute values, highlighting column and row headers (<th> elements) and differentiating them each other and from the data cells (<td>).
th,
td {
border: 1px solid rgb(160 160 160);
padding: 8px 10px;
}
th[scope="col"] {
background-color: #505050;
color: #fff;
}
th[scope="row"] {
background-color: #d6ecd4;
}
tr:nth-of-type(odd) td {
background-color: #eee;
}
Result
Column and row spanning
This example extends and enhances the basic table from the previous example by adding a second row for additional column headers.
HTML
An additional table row (<tr> element) is added as the second header row of the table with two additional column headers (<th> elements). In this way, the "Pronunciation" column is split into two columns, one for the IPA (International Phonetic Alphabet) notation and one for the respelling (the original pronunciation column). The corresponding data cells (<td> elements) are added to each subsequent row.
As shown in the usage notes, the colspan and rowspan attributes can be used for the <th> elements to allocate the header cells to the correct columns and rows. To achieve a "two-row" header in the table structure, the first two header cells within the first <tr> element are spanned across two rows. The third header cell is spanned two columns wide (remaining in the first row). This setup leaves two available areas in the third and fourth columns in the second row, where the two headers within the second <tr> element are automatically placed, with the default value being 1 for the colspan and rowspan attributes.
Note: Normally, <thead> and <tbody> elements are used to group rows with headers into the respective table head and body sections. This is not implemented in this example to focus on the headers and spanning and reduce the example's complexity.
<table>
<tr>
<th scope="col" rowspan="2">Symbol</th>
<th scope="col" rowspan="2">Code word</th>
<th scope="col" colspan="2">Pronunciation</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<th scope="col">IPA</th>
<th scope="col">Respelling</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<th scope="row">A</th>
<td>Alfa</td>
<td>ˈælfa</td>
<td>AL fah</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th scope="row">B</th>
<td>Bravo</td>
<td>ˈbraːˈvo</td>
<td>BRAH voh</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th scope="row">C</th>
<td>Charlie</td>
<td>ˈtʃɑːli</td>
<td>CHAR lee</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th scope="row">D</th>
<td>Delta</td>
<td>ˈdeltɑ</td>
<td>DELL tah</td>
</tr>
</table>
CSS
The CSS is unchanged from the previous example.
Result
Associate header cells with other header cells
For more complex relationships between header cells, using th elements with the scope attribute alone may not be sufficient for assistive technologies, especially screen readers.
HTML
To improve the accessibility of the previous example and to allow screen readers, for example, to speak the headers associated with each header cell, the headers attribute can be introduced along with id attributes. Because of the way the "Pronunciation" column is split into two columns in the example, introducing a "two row" header, assistive technologies such as screen readers may not be able to identify which additional header cells (th elements) the "Pronunciation" header cell is related to and vice versa. Therefore, the headers attribute is used on the "Pronunciation", "IPA", and "Respelling" header cells to associate the related header cells based on the values of the unique identifiers from the added id attributes in the form of a space-separated list.
Note: It's recommended to use more descriptive and useful values for the id attribute. Each id in a document must be unique to that document. In this example, the id values are single characters to maintain focus on the concept of the headers attribute.
<table>
<tr>
<th scope="col" rowspan="2">Symbol</th>
<th scope="col" rowspan="2">Code word</th>
<th scope="col" colspan="2" id="p" headers="i r">Pronunciation</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<th scope="col" id="i" headers="p">IPA</th>
<th scope="col" id="r" headers="p">Respelling</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<th scope="row">A</th>
<td>Alfa</td>
<td>ˈælfa</td>
<td>AL fah</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th scope="row">B</th>
<td>Bravo</td>
<td>ˈbraːˈvo</td>
<td>BRAH voh</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th scope="row">C</th>
<td>Charlie</td>
<td>ˈtʃɑːli</td>
<td>CHAR lee</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th scope="row">D</th>
<td>Delta</td>
<td>ˈdeltɑ</td>
<td>DELL tah</td>
</tr>
</table>
Result
The visual result is unchanged from the previous example table.
Technical summary
| Content categories | None. |
|---|---|
| Permitted content | Flow content, but with no header, footer, sectioning content, or heading content descendants. |
| Tag omission |
The start tag is mandatory. The end tag may be omitted, if it is immediately followed by a <th> or
<td> element or if there are no more data in its
parent element.
|
| Permitted parents | A <tr> element. |
| Implicit ARIA role | columnheader or rowheader |
| Permitted ARIA roles | Any |
| DOM interface | HTMLTableCellElement |
Specifications
| Specification |
|---|
| HTML Standard # the-th-element |
Browser compatibility
BCD tables only load in the browser
See also
- Learn: HTML tables
<caption>,<col>,<colgroup>,<table>,<tbody>,<td>,<tfoot>,<thead>,<tr>: Other table-related elementsbackground-color: CSS property to set the background color of each header cellborder: CSS property to control borders of header cellsheight: CSS property to control the recommended header cell heighttext-align: CSS property to horizontally align each header cell contentvertical-align: CSS property to vertically align each header cell contentwidth: CSS property to control the recommended header cell width:nth-of-type,:first-of-type,:last-of-type: CSS pseudo-classes to select the desired header cells